515
Views & Citations10
Likes & Shares
Toys and games have been a part of human civilization for thousands of years, and ancient societies had their versions of playthings. Toys have been found in archaeological sites across the Indian subcontinent, dating back to the Indus Valley Civilization (3300–1300 BCE). Archaeological excavations have revealed small toys made of clay, stone, wood, and terracotta that were used by children during this era. The Harappan civilization, which was part of the Indus Valley civilization, produced a variety of toys including wheeled toys, animal figures, and dolls. These toys depict various aspects of daily life and provide insights into the culture and society of that era. Besides, traditional Indian games such as Pachisi (a precursor to the modern-day game of Ludo), Snakes and Ladders, and Chaturanga (a precursor to the widely popular game today known as Chess) have their roots in ancient times. From mythology to history, these games have appeared all over India depicting stories from epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata.
During the medieval period, toy-making centers emerged in various parts of India, such as Channapatna in Karnataka, Kondapalli in Andhra Pradesh, and Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, along with Delhi, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and West Bengal. Wooden toys, such as dolls, puppets, and animals, were popular in these regions. These toys were made using local materials and techniques that were specific to each region.
With the arrival of European traders and colonizers in India, new influences and materials were introduced, impacting toy-making in the country. European-style dolls, board games, and mechanical toys started to be manufactured in India, combining traditional craftsmanship with new techniques. After India gained independence in 1947, the toy industry in the country witnessed further growth and diversification. Traditional toys continued to be made, but there was also an influx of mass-produced plastic toys from around the world.
In the modern era, toys and games encompass a wide range of options that cater to various interests, age groups, and developmental needs such as electronic & battery-operated toys, STEM toys, interactive plush toys, Augmented reality (AR) & Virtual reality (VR) toys, Puzzle and brain teaser games, etc. The selection continues to evolve with advancements in technology, catering to various interests and learning objectives.
Overall, Indian toys have a deep-rooted history that reflects the country's cultural diversity and artistic traditions. They continue to be integral to childhood experiences, connecting generations and preserving the heritage of India's toy-making traditions. Efforts are also being made to revive and promote traditional toys, as they not only provide a source of entertainment and pleasure but also carry cultural and educational value, showcasing the artistic skills and creativity of Indian artisans.
CURRENT SCENARIO
The Toys& Games market amounts to US$ 1,623million in 2023. The market is expected to grow annually by 5.11 per cent (CAGR 2023-2028). The Indian toys industry comprises more than 4,000 manufacturing units that include 75 per cent micro, 22 per cent small and medium, and 3 per cent large units. Under the Ministry of MSME’s Scheme of Funds for Re-generation of Traditional Industries (SFURTI), an outlay of INR 41.60 crores has been allocated to a total of 14 manufacturing clusters to benefit 8,839 artisans by providing aid in terms of the latest machines, design centers, raw material bank, and skill development programs. The Office of Development Commissioner (Handicrafts), Ministry of Textile, is also developing infrastructural support for the artisans of handmade toys in India.
The Indian Prime Minister highlighted the immense future potential of Indian toys in his ‘Mann Ki Baat’ address broadcast on August 30th, 2020. Prime Minister Narendra Modi urged Indians, particularly start-ups, to be "vocal for local for toys," stating the country's rich heritage & customs as potential drivers of innovation in the global toy business, and thrust upon how it can further the spirit of ‘Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat’ (One India, Strong India). He added that while Global Toy Industry is worth more than 7 lakh crore rupees, India currently has a negligible share. While discussing the computer game trend, Prime Minister proposed creating games based on ideas and concepts from our historyhttps://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1649746. Since then, several measures were taken to boost India’s toy production. Later, in July 2022, The Prime Minister described India's toy sector success as "unprecedented," with exports increasing from INR 300-400 crores to INR 2,600 crores and imports falling sharply by 70 per cent from Rs 2960 crores in 2018-19 to Rs 870 crores in 2021-22 https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1845398.
According to a joint report by KPMG and FICCI, the Indian toy industry had a market size of USD 1 billion in 2019-20 and is expected to double to USD 2 billion by 2024-25. The report also mentioned that, by 2025, India might potentially aim for a 2 per cent share of global exports. India has significant development potential in exports of plastic toys and board games to the United States, the European Union, and the Middle East, among other countries.
CLASSIFICATION OF TOYS& GAMES IN INDIA
Indian toys, which are made throughout the country, exhibit cultural diversity in the variety of goods available. Toys manufactured in India now include plastic, mechanical, soft/plush dolls and animals, board games, puzzles, educational games, metal and tin, wood, battery-driven pullback toys, and so on. Indian toys are made from a variety of raw materials, including plastic, wood, rubber, metals, and textiles, with a large share of enterprises being clubbed with MSMEs. Traditional toys are also a significant cultural treasure since they illustrate ancient mythological stories and reflect community beliefs and traditions. Traditional toys appeal to consumers because they allow them to preserve their history, while craftsmen and artisans rely on manufacturing for a living.
In this study, we refer exclusively to the type of Toys & Games manufactured in India that require some kind of physical equipment for playing.
Toys & Games have been broadly classified into Recreational and Educational toys. Educational toys are classified based on the skills and concepts they target such as counting beads, abacus, construction toys, puzzles, word-building games, brain teaser games, etc. Recreational toys on the other hand are designed primarily for entertainment and leisure purposes. These toys provide opportunities for children to have fun, engage in play, and unwind. These include dolls, dollhouses, action figures, plush toys, electronic (video games, remote control), battery-operated toys, water toys, ride-on toys, etc.
Although a large variety of Toys & Games are available in the market, the study will be exclusively focusing on imports and exports of Toys & Games under Harmonized System (HS) Code 95 including Toys, Games, and Sports Requisites; Parts and Accessories thereof.
SUSTAINABILITY OF INDIAN TOYS
Sustainability is an upcoming potential trend setter in the toys industry. A range of environment-friendly products, including wooden baby toys, plastic-free games for kids, recycled plastic bath games, and organic cotton stuffed animals, are increasingly becoming popular, thereby promoting sustainability https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/toys-hobby/toys-games/india. By embracing sustainability in the toys industry, India can continue to preserve its cultural heritage, support local artisans, and contribute to a greener and more inclusive future. The sustainability of Indian toys can be examined from multiple perspectives, including environmental, social, and economic aspects.
ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Use of Natural and Biodegradable Materials: Most of the traditional Indian toys are crafted using natural and biodegradable materials like wood, clay, bamboo, and natural dyes. These materials have minimal environmental impact compared to plastic toys, contributing to long-term pollution and waste.
Low Carbon Footprint: Traditional toy-making processes in India often involve local artisans using hand tools and techniques, which consume less energy and have a lower carbon footprint compared to mass-produced plastic toys.
Recycling and Upcycling: Indian toys, especially those made from materials like wood and clothes, can often be repaired, reused, or repurposed, reducing waste and extending their lifespan. Some Indian toy makers create toys using upcycled or recycled materials. They repurpose items like cardboard, paper, fabric scraps, and plastic bottles to create unique and sustainable toys. These toys promote waste reduction and creativity.
SOCIAL SUSTAINABILITY
Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Despite being the originator of several worldwide recognized games such as Chess, Ludo, Snakes & Ladders, etc., India is not among the major toy manufacturers. Supporting and promoting these toys can contribute to the preservation of traditional craftsmanship, indigenous knowledge, and cultural diversity.
Empowering Artisans and Communities: Toy-making is often a cottage industry in India, providing livelihood opportunities for artisans and their communities. By purchasing Indian toys, we support these artisans and help sustain their skills, income, and local economies in a sustainable manner.
Educational and Skill Development: Indian toys, particularly those based on traditional games and puzzles, can have educational value. They stimulate creativity, problem-solving, and fine motor skills, promoting holistic development among children.
ECONOMIC SUSTAINABILITY
Domestic Support: Buying Indian toys supports local toy manufacturers, artisans, and small businesses. This contributes to the growth of the domestic toy industry, fostering economic sustainability and self-reliance.
Export Potential: Indian toys, with their unique designs, craftsmanship, and eco-friendliness, have the potential to be exported to international markets, generating foreign exchange and boosting the country's economy.
In recent years, there has been growing awareness and appreciation for sustainable toys globally, including in India. Efforts are being made to promote eco-friendly and socially responsible toy-making practices, encourage innovation in sustainable materials, and revive traditional toy-making techniques. While sustainable and eco-friendly toys are growing in popularity, they may be relatively more expensive than mass-produced plastic toys. However, their durability, non-toxic nature, and positive impact on the environment make them a worthwhile investment.
FACTORS DRIVING GROWTH OF INDIAN TOYS SECTOR
Domestic Market Potential
India is home to one of the youngest populations in the world, implying that the number of children is expected to increase in the coming years. Rising disposable income and changing lifestyles have increased the demand for toys in the domestic market. Moreover, the expanding middle-class population in India presents a substantial consumer base for toys. As the middle class expands, there is a greater capacity for discretionary spending on toys.
Shift towards STEM Toys
There has been a noticeable increase in awareness and demand for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) toys in recent years. These toys provide engaging and interactive learning experiences, preparing children for a world that increasingly relies on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. STEM toys are a fun and interactive way for children to engage with these subjects, fostering curiosity, creativity, and critical thinking skills necessary for the 21st century workforce. As a result, parents, educators, and policymakers emphasize the need to promote STEM learning from an early age. This is because STEM toys provide a hands-on and engaging way for children to explore these subjects and develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Employment Generation
Since the domestic toy industry is labor intensive, it can provide employment opportunities to many people, particularly in the informal sector. Artisans, craft persons, and small-scale manufacturers constitute a significant portion of the industry's employment.
Technological Integration
The use of technology in toys provides new potential for growth. Manufacturers may enhance the play experience and attract tech-savvy children and parents using augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), robotics, and interactive elements. Adopting online platforms for marketing and distribution will help Indian toys attract a broader consumer base.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has initiated several measures to facilitate the growth of the toys sector. This includes promoting the "Vocal for Local" campaign, launching the National Toy Fair, organizing Toycathon, and enacting regulations to encourage indigenous toy manufacture. These measures have established a platform for local toy producers and a favorable industry growth climate.
POLICY INITIATIVES
The recent revival in the toys industry exemplifies the success of the government's targeted strategy to promote domestic manufacturing. Since our Prime Minister's appeal to the industry, businesses, and start-ups, to ‘team up for toys’ and make the nation a global toy and gaming hub, there has been much progress in the formerly low-profile industry. The Prime Minister urged the people to focus on the production of Toys & Games based in and for India, stating that we import the majority of toys consumed in the country, resulting in a loss of foreign exchange worth crores of rupees https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/toys-hobby/toys-games/india. As a result, the Indian government has undertaken various initiatives to promote the country's toy industry. Such initiatives aim to increase local manufacturing, promote traditional Indian toys, enforce quality and safety standards, and create a favorable climate for toy producers to expand their export prospects. Some of these initiatives are as follows
National Action Plan for Toys
‘The National Action Plan for Toys (NAPT) 2020’ is a comprehensive plan launched to boost the Indian toy industry, including traditional handicrafts and handcrafted toys, to establish India as a worldwide toy hub. The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), in collaboration with 14 Central Government ministries, is presently executing its various aspects. The National Action Plan for Toys addresses several issues, including the following:
- Creating toys as a learning resource.
- Designing toys based on Indian culture, tradition, and values.
- Organizing toy fairs, hackathons, and exhibitions promoting innovation in designing and manufacturing.
- Creating awareness regarding indigenous toys such as puppets, wooden dolls, clay toys, tribal games, etc., and increasing production.
- Setting up toy clusters and repository centers across the country.
- Launching Central Government schemes to incentivize and upskill local artisans in manufacturing and exports.
- Monitoring quality and safety standards of toys.
- Promoting sustainable toys using recycled and plastic-free materials.
- Promoting toy tourism.
- Promoting investments and exports of Indian toys.
- Promoting virtual, digital, and online gaming that matches India's philosophy.
The India Toy Fair
On 27th February 2021, Prime Minister launched The India Toy Fair, a first-of-its-kind initiative to bring together all stakeholders in the Indian toy industry on a virtual platform to foster long-term sustainable linkages and stimulate discourse for the sector's overall development. The Toy Fair was held on a virtual/digital platform to increase toy production in India. Participants had the opportunity to meet with toy exhibitors from various toy clusters in India during the event. The Toy Fair attracted more than 1,000 exhibitors, which included Toy Clusters; Crafts persons; Manufacturers; Exporters; Fair Trade Organizations; Self Help Groups (SHGs); Associations / Promotional Organizations such as EPCs/Boards/State Corporations / Chambers; Doll Museums / Toy Stores; Design Centers; Stat ups like Smartivity / Skillmatics; as well as partner states https://www.ibef.org/blogs/national-action-plan-to-accelerate-india-s-toy-sector. The main objective of the fair was to get the industry and the government together to figure out how to make the country the next worldwide powerhouse for toy manufacturing and sourcing. The Fair would also aid in the attraction of investments and the promotion of exports.
Toycathon
Toycathon was launched in January 2021 as a first-ever hackathon to rediscover/redesign traditional Indian toys based on Indian civilization, history, culture, mythology, and ethos. It is an inter-ministerial initiative organized by the Ministry of Education's Innovation Cell with support from the Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the Ministry of MSME, the Ministry of Textiles, and the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting to crowd-source solutions to problems faced by the toy industry. Toycathon 2021 was aimed at conceptualizing innovative toys based on the Indian value system that instills positive behavior and values among youngsters. Later, the ‘Swachh Toycathon’ competition was also launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs as a convergence between National Action Plan for Toys and Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM 2.0) that seeks to explore solutions for the use of waste in the creation or manufacturing of toys.
Toys Quality Control Order
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, has issued the Toys Quality Control Order (QCO), 2020 under Section 16 of the BIS Act, 2016. This Quality Control Order requires children’s toys to adhere to seven Indian Standards for the safety of toys and to wear the ISI Mark under a BIS license. The QCO came into effect on January 1, 2021. As a result, no one is entitled to manufacture, import, sell or distribute, store, hire, lease, or exhibit for sale of toys that do not adhere to the Indian Standard and do not bear the "ISI" mark under a BIS license https://www.ibef.org/blogs/national-action-plan-to-accelerate-india-s-toy-sector. Toys covered under the TQCO must undergo testing and certification from authorized laboratories to ensure compliance with safety standards. The certification process verifies the quality, safety, and compliance of toys with the prescribed regulations.
SFURTI
The SFURTI (Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries) scheme in India has been implemented by the Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME). The SFURTI scheme for toys in India aims to revive and promote traditional toy-making crafts, improve the livelihoods of artisans, and promote the heritage and cultural value of Indian toys. Financial assistance is provided under this scheme for project activities such as infrastructure development, machinery, and equipment procurement. Following are some of the features of this scheme:
- Enhancing the competitiveness of traditional toy industries
- Conserving and preserving traditional toy-making crafts and skills
- Upgrading the technology and skills of artisans
- Promoting market access and marketing of traditional toys.
The scheme is implemented by setting up Common Facility Centers (CFCs) in the toy clusters. The CFCs are established to provide common production facilities and services to artisans and toy manufacturers. The CFCs are outfitted with modern machinery, tools, and equipment to enhance productivity and quality. Traditional toy-making clusters, associations, self-help groups, cooperatives, etc., can apply for support under the scheme.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
The Indian government has recently launched the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for the toys industry to enhance productivity and promote domestic manufacturing. It aims to attract investment, boost export potential, and create employment opportunities in the toys sector. The incentives provided under the scheme will help manufacturers improve their competitiveness by investing in advanced technologies, research and development, design capabilities, and quality improvement. To participate in the PLI scheme, toy manufacturers must meet certain eligibility requirements, including investment and sales thresholds, compliance with quality standards, and adherence to various statutory and environmental norms. The PLI scheme will aid in developing an ecosystem for the toy manufacturing industry, allowing for the production of high-quality toys for both domestic and worldwide markets.
Trade Pattern of Toys Industry
The imports and exports of the Indian Toys Industry have been analyzed by calculating the Annual Growth Rate of Toys, Games, and Sports requisites; parts, and accessories thereof (HS Code 95). The data for imports and exports of Toys & Games under HS Code 95 has been obtained from the Export-Import Data Bank, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India (Figure 1).
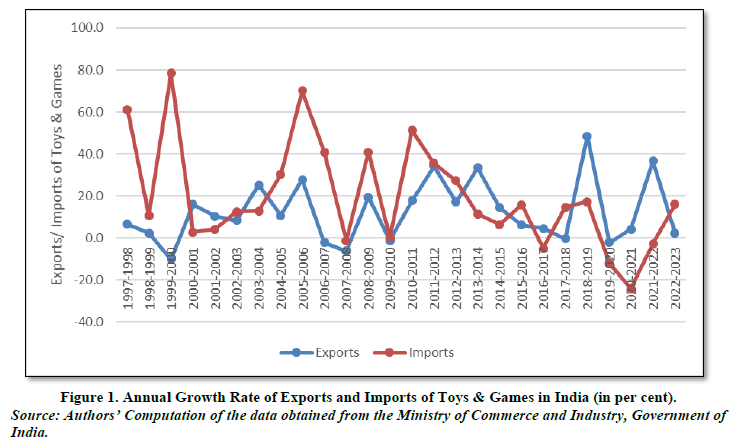
The above graph Figure 1 shows the annual growth rate of exports and imports of Toys & Games in India from 1997-98 to 2022-23. Over the years, the imports and exports of toys have shown a cyclical pattern. During the initial years, toy imports increased at a faster rate than exports. For the period 2010-11 to 2018-19, there has been a steady decline in the imports of toys. In 2018-19, the exports of toys recorded an all-time high annual growth rate of 48.4 per cent. Since 2019-20, toy exports increased significantly making India a net exporter of toys till 2021-2022. The imports fell sharply from 2018-19 to 2020-2021. The imports of toys were at the lowest in the year 2020-21 with an annual growth rate of -24.2 per cent. This decline in imports was driven by a hike in the Basic Customs Duty on toys from 20 per cent to 60 per cent by the Government in 2020, which was accompanied by the outbreak of COVID 19 pandemic.
CONCLUSION
The Indian toy industry has made significant achievements in its growth and development. Over the years, various factors, including government initiatives, market demand, and innovation, have contributed to the industry's success. Toy manufacturers are now concentrating on creating toys with educational value, interactive features, and distinctive designs. This shows an increasing transition toward high-value, creative products in this sector. This transition is driven by shifting consumer tastes and rising recognition of the significance of play in child development.
The export potential of Indian toys has opened up new avenues for growth, attracting investments and encouraging innovation in the sector. To capitalize on these potential prospects, the Indian toy sector may benefit from favorable government policies, investment in R&D, skill development initiatives, and collaboration with educational institutions and industry organizations. By leveraging these opportunities, the Indian toy industry can further strengthen its position in the global market.
India offers several advantages, including ample raw materials, low labor costs, and a diverse choice of products to choose from. However, the industry has its own set of obstacles. Furthermore, despite the focused interventions of the government, the growth remains slow due to the highly fragmented nature of the industry. Moreover, it faces challenges with fragmented technical knowledge and despite high demand, it remains largely unorganized. The industry struggles to produce volumes for globally competitive pricing.
To realize its potential, the industry needs to address these challenges. Efforts are required to enhance technical knowledge, promote collaboration, and establish streamlined processes and quality standards. Skill development programs, capacity building, and access to finance can support industry growth. In addition, a specific national-level policy for the manufacture of toys is required. Such a policy may cover various concerns and provide a complete framework for the sector to address issues such as development, sustainability, and competitiveness.
Overall, the Indian toy industry is witnessing growth and is focused on sustainability, cultural preservation, and economic development. Efforts are being made to revive traditional toy-making crafts, empower artisans, and position India as a global hub for toy manufacturing.
https://toycathon.mic.gov.in/index.php
https://www.ibef.org/blogs/national-action-plan-to-accelerate-india-s-toy-sector
https://www.investindia.gov.in/team-india-blogs/indias-booming-toyconomy
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1845398
https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/toys-hobby/toys-games/india
India achieving Aatmanirbharta in sunrise sectors Toy and Gaming Sector. Available online at: https://pib.gov.in/FeaturesDeatils.aspx?NoteId=151133&ModuleId%20=%22
Indian Standards on Toys Ensuring Your Child’s Safety. Available online at: https://www.services.bis.gov.in/php/BIS_2.0/BISBlog/
The India Toy Fair Virtual (2021). e CRAFTCIL. Available online at: https://www.epch.in/ecraftcil/issue78/index.html
Trends in Shaping the Toy Industry Outlook in (2021). https://plexconcil.org/public/custom/images/articles/pdf/1613107271.pdf